China use drones to deliver fast food to homes !!
During our school days , the drone that what I know was a flying machine with four rotor fans which carry a camera to shoot a wedding ceremonies . This type of simple drone cost now Rs 25,000/= and weighs 400 gms. Drone was a symbol of high end marriage photography and video shoot. Watching arial view of marriage function was a treat to eyes. Very recently Drones were heavily used for crowd management in Maha Kumbh 2025 in India .

Military Drones –
But now drones are not for peaceful purpose only , but are being used to kill enemy in the battle field. Some of the simple army drones can carry deadly bombs of 20 Kg and fly more than 100 Km and drop the bomb/missile in the enemy area. Now a days Army use drones as their main attacking machine. In recent four day conflict between India and Pakistan. Pakistan used more than 700 Drones to attack India cross the border. Medium size army drone with explosive cost minimum $20,000/= . Ukraine and Russia are attacking each other using deadly drone ( Kamikaze type ) which are reaching Kiev / Moscow undetected.

Types of Drones –
Drones come in many types, categorized by their design, use-case, and capability. Here’s a details the most common types:
- Multi-Rotor Drones
- Most common (e.g., quadcopters)
- Used for photography, surveillance, and hobby flying
- Now a days used by fast food delivery company in some of the countries.
- Was introduced in market late 1990 to shoot wedding and gathering.
- Fixed-Wing Drones
- Look like airplanes; can glide and cover long distances
- Used for mapping, agriculture, and military applications
- Fixed-Wing Hybrid VTOL Drones
- Combine vertical take-off/landing with fixed-wing flight
- Suitable for delivery and inspection tasks
- Single-Rotor Helicopter Drones
- More complex; often used for heavier payloads
- Used in industrial or military contexts
- Nano / Micro Drones
- Small drones, often for indoor or reconnaissance purposes
- Used in research, military, or toy industries

By Usage –
- Consumer Drones
- For photography, videography, or hobby flying
- Commercial Drones
- Used in agriculture, construction, real estate, logistics , fast food delivery.
- Industrial Drones
- For heavy lifting, inspections (power lines, wind turbines)
- Military Drones (UAVs)
- Used for surveillance, combat, reconnaissance , military attacks.
- Delivery Drones
- Used by companies like Amazon, UPS , pizza hut , McDonald for last-mile delivery
- Racing Drones
- Built for speed and agility; used in competitive drone racing
- Underwater Drones (ROVs/AUVs)
- Operate underwater for exploration, inspection, research , attacking ships and other type of underwater sabotage .
Drones for General Public –
Drones used for civilian purposes and civil administration vary depending on their specific applications. Here’s a breakdown by use-case:
- Consumer Drones
- Type: Multi-rotor (usually quadcopters)
- Use: Photography, videography, recreational flying
- Drones Racing
- Type: Small, fast FPV drones
- Use: Competitive racing, sports
- Hobbyist/Nano Drones
- Type: Micro or nano quadcopters
- Use: Indoor flying, beginner training
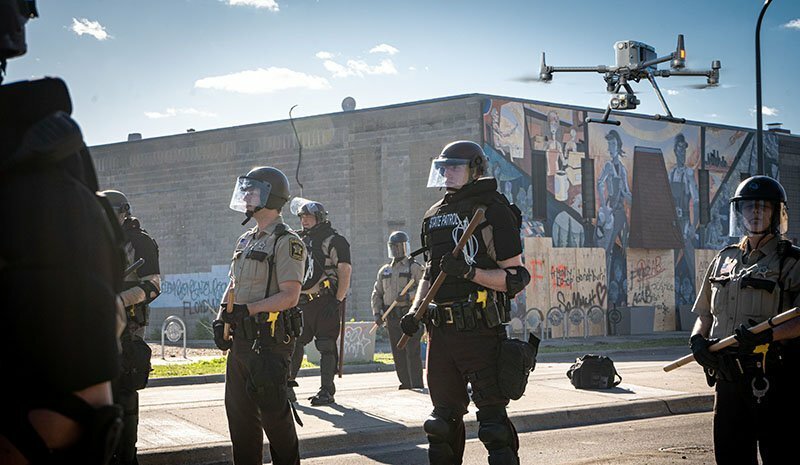

Drones for Civil Administration –
These drones are used by government departments and public services (non-military):
1. Surveillance & Law Enforcement
- Used by: Police, border patrol, disaster management
- Type: Multi-rotor and fixed-wing drones with thermal/night vision
- Functions: Crowd monitoring, search and rescue, crime scene mapping
2. Disaster Response & Search and Rescue (SAR)
- Used by: Fire departments, emergency services
- Type: Multi-rotor drones with thermal imaging and loudspeakers
- Functions: Locate victims, assess damage, deliver supplies
3. Infrastructure Inspection
- Used by: Public works, transportation departments
- Type: Industrial drones (often VTOL or multi-rotor)
- Functions: Bridge, dam, road, and building inspection

4. Agricultural Monitoring
- Used by: Agriculture departments
- Type: Fixed-wing or hybrid drones with multispectral sensors
- Functions: Crop health monitoring, irrigation planning & Pesticide spray
5. Land Surveying & Mapping
- Used by: Survey and land record departments
- Type: Fixed-wing drones or RTK-enabled multi-rotors
- Functions: Topographic mapping, cadastral surveys, urban planning
6. Environmental Monitoring
- Used by: Environmental agencies
- Type: Fixed-wing or multi-rotor drones with sensors
- Functions: Air quality testing, wildlife tracking, forest monitoring
Cost of domestic Drones – Cost of different type of Drome for civil use range from $200 to $2,500 depending upon quality , range & capacity of Camera to operate .
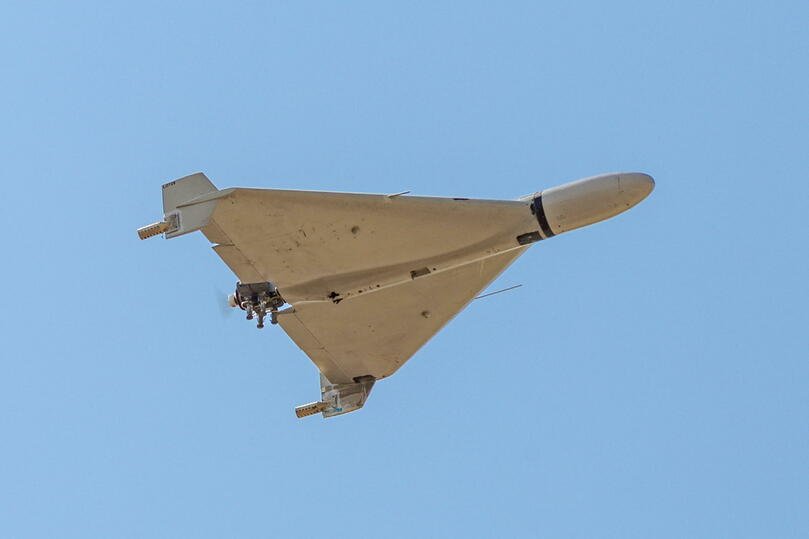

Military Drones –
Types of Drones Used by the Army (UAV Military Drones)
Military drones, also known as UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles), are used for surveillance, reconnaissance, combat, logistics, and intelligence gathering. They are generally more advanced and expensive than civilian drones. Most of UAV drones are operated from a control room 1,000s of KM away from the battle field.
1. Surveillance & Reconnaissance Drones
Used for intelligence gathering, monitoring enemy movement, and battlefield awareness.
- Examples:
- RQ-4 Global Hawk (USA): High-altitude, long-endurance ISR drone.
- Heron (Israel/India): Medium-altitude, long-endurance drone.
- ScanEagle (USA): Small drone for tactical surveillance.
- RQ-7 Shadow (USA): Used for day/night aerial surveillance.
2. Combat Drones (Armed UAVs)
Used for precision airstrikes and targeted operations.
- Examples:
- MQ-9 Reaper / Predator B (USA): Armed with Hellfire missiles, bombs.
- Bayraktar TB2 (Turkey): Used by several countries; successful in many conflicts.
- Wing Loong II (China): Armed and used for both surveillance and strikes.
- Elbit Hermes 900 (Israel): Can be armed, also used for reconnaissance.
3. Tactical Mini / Loitering Drones
Smaller drones used by infantry units on the ground; some are expendable.
- Examples:
- Black Hornet Nano (USA/NATO): Palm-sized, used for close-range recon.
- Switchblade 300/600 (USA): “Kamikaze drone” that loiters and attacks targets.
- Warmate (Poland): Tactical loitering munition (drone bomb).
4. Logistics and Supply Drones
Used for delivering medical supplies, ammunition, or communication gear to the battlefield.
- Examples:
- AeroVironment Puma AE (USA): Small drone with variants used for comms and supply drops.
- Experimental quadcopters for payload delivery in contested zones.
5. Electronic Warfare and Decoy Drones
Used to jam enemy radar or act as decoys to confuse defence systems.
- Examples:
- MALD (Miniature Air-Launched Decoy) – simulates aircraft radar signatures.
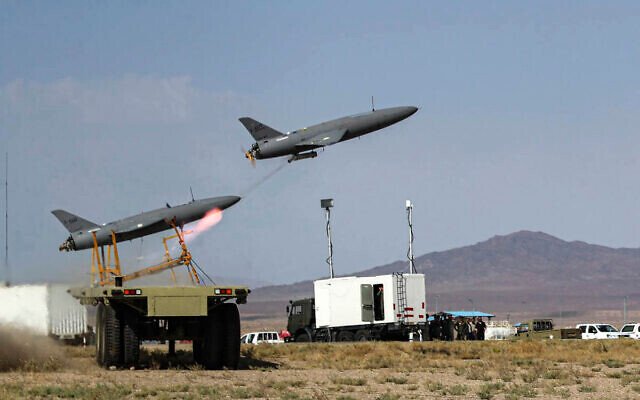
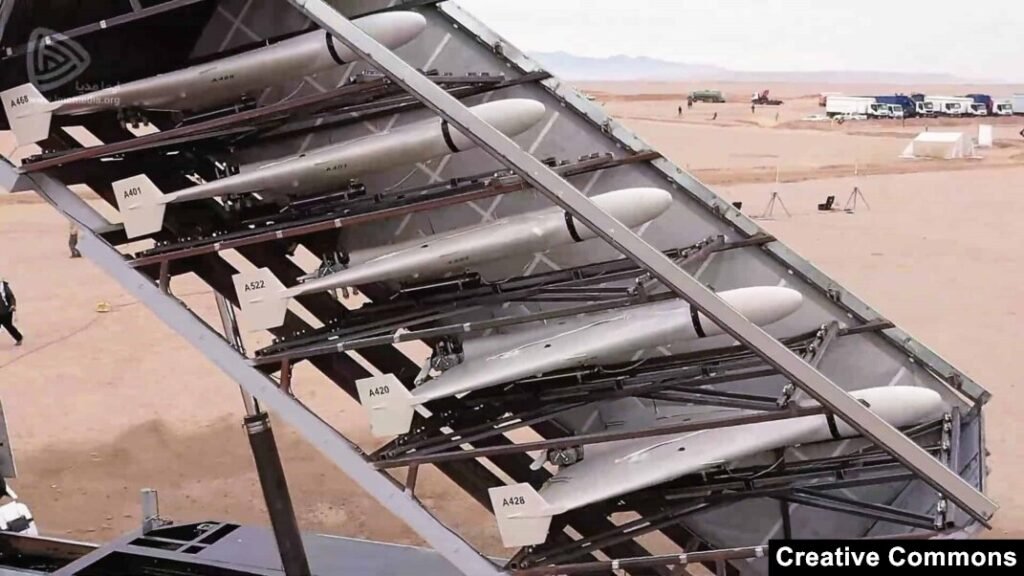
- Shahed-136 (Iran/Russia): Loitering munition also used to saturate defenses.

UAV Drone Cost
Military drones vary widely in cost, influenced by their size, capabilities, and intended roles.
- Small tactical drones: $10,000–$100,000
- Medium surveillance drones: $1–5 million
- Armed drones: $5–30 million depending on payload and range
Many Countries have unmanned arial vehicle (UAV) , which is the advance form of drone . UAV are auto pilot can fly non stop for more than 5-10 hours , spy on enemy country , take pictures and even used bombs /missiles to attack and return back to the base. Some of the UAV can not be detected by Radars .
Drone War – Russia Vs Ukraine Top of Form
The war in Ukraine has witnessed an unprecedented scale of drone deployment by both Ukrainian and Russian forces, fundamentally transforming modern warfare.

Ukraine’s Drone Utilization
- Production and Supply: In 2024, Ukraine’s Defense Ministry supplied approximately 1.2 million Drone to its military forces.
- Loss Rates: Estimates indicate that Ukraine has been losing around 10,000 drones per month, amounting to over 100,000 drones annually.
- Types and Roles: Ukraine employs a diverse array of drones, including small FPV (First Person View) drones for reconnaissance and attack missions, as well as larger UAVs like the Bayraktar TB2 for long-range strikes. These drones are integral to various military operations, from surveillance to direct attacks on enemy targets.
- Offensive Operations: Since the onset of the conflict, Ukrainian forces have utilized at least 9,700 drones to strike targets within Russian territory, showcasing the strategic offensive use of UAVs
Russia’s Drone Deployment
- Shahed Drone Usage: Between August 1, 2024, and March 1, 2025, Russia launched approximately 15,011 Shahed-type strike UAVs against Ukrainian targets.
- Escalation of Attacks: Starting in September 2024, Russia significantly increased its drone attacks, escalating from about 200 launches per week to over 1,000 per week by March 2025.
Impact on modern Warfare
Drones have become a dominant force on the battlefield, responsible for approximately 80% of all casualties in the Ukraine war. Their extensive use for surveillance, precision strikes, and electronic warfare has redefined combat strategies and highlighted the evolving nature of military engagements.

Modern Wars are Drone Based –
Modern warfare is increasingly being shaped by drones, and future conflicts are expected to rely even more heavily on them. Why Drones Are Central to Modern War . Here’s why:
Cost-Effective & Low-Risk
- Drones can perform missions without risking pilots’ lives.
- Some models (like loitering munitions or quadcopters) cost a fraction of traditional weapons or aircraft
Versatility
- Drones are used for:
- Surveillance & reconnaissance
- Precision strikes
- Electronic warfare
- Logistics (e.g., resupplying frontline troops)
- Swarm attacks (many small drones attacking at once)
Adaptability in Asymmetric Warfare
- Countries or groups with fewer resources can use drones to challenge advanced militaries.
- Example: In Ukraine, cheap commercial drones have been modified for bombing and recon.
AI and Autonomy
- AI-driven drones can:
- Identify targets autonomously
- Navigate without GPS
- Operate in coordinated swarms
Stealth and Reach
- Long-range drones can penetrate deep into enemy territory with low radar visibility.
Real-World Examples
- Ukraine-Russia War: Widely seen as the world’s first “drone war” with thousands of drones used daily.
- US Operations: Rely heavily on MQ-9 Reaper and others for counter-terrorism.
- Azerbaijan-Armenia Conflict: Turkish Bayraktar TB2 drones were decisive.
- Houthi Rebels: Used Iranian drones to strike oil infrastructure in Saudi Arabia.
Limitations of Drones
- Vulnerable to electronic warfare and anti-drone defences
- Ethical concerns over autonomous kill decisions
- Dependency on satellites/GPS, which could be targeted

Conclusion :
Drones have become a dominant force on the battlefield. It was responsible for approximately 80% of all casualties in the Ukraine war. Their extensive use for surveillance, precision strikes, and electronic warfare has redefined combat strategies and highlighted the evolving nature of military engagements.
The friendly drone which used to shoot wedding ceremonies during my school days is no more friendly, it has become a monster flying machine killing humans in the wars.