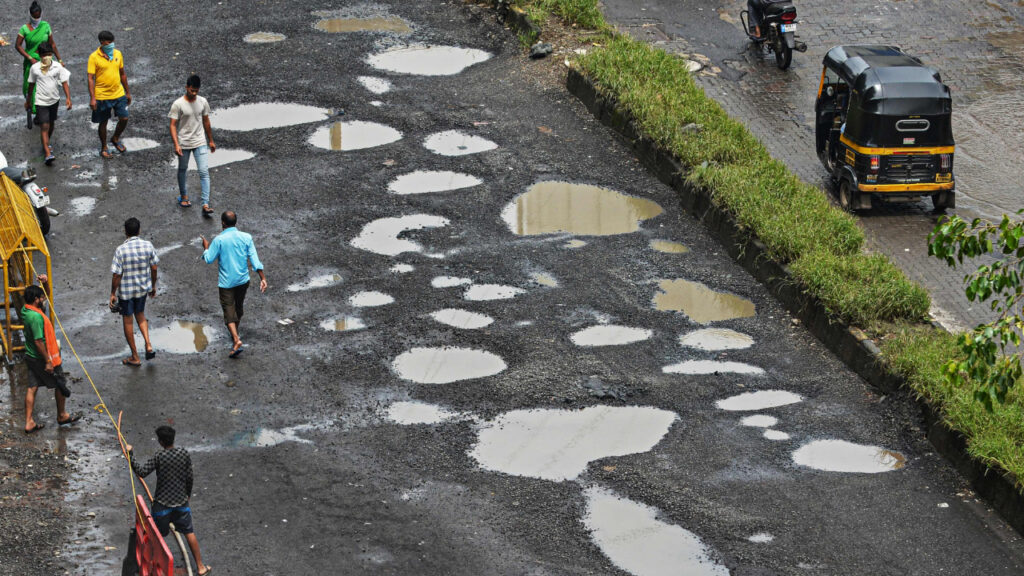
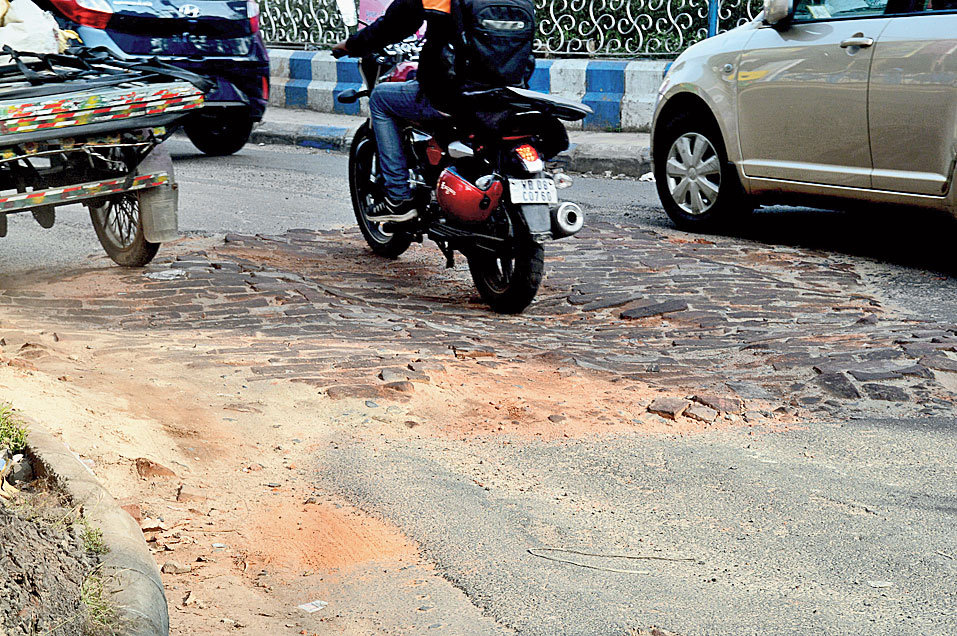
Standing water is the enemy of Asphalt Roads
India stand ranked 52 out of 100 in quality of Roads . India has second largest road networks in the world . India claims 4th largest World’s economy but I doubt so by looking at potholes on the roads . There is no town , city , villages or connecting city roads where there is no Potholes . Indian govt spend more than Rs 280,000 Crores every years on roads but overall quality of roads are bad to worse. Laying one additional layer of Asphalt over old damage and dirty road will not give us good quality roads , I call it cosmetic makeup. 2000 Year old Roman roads in Europe are still intact and our many new roads constructed last years has multiple potholes or washed away with heavy Rain , why ?

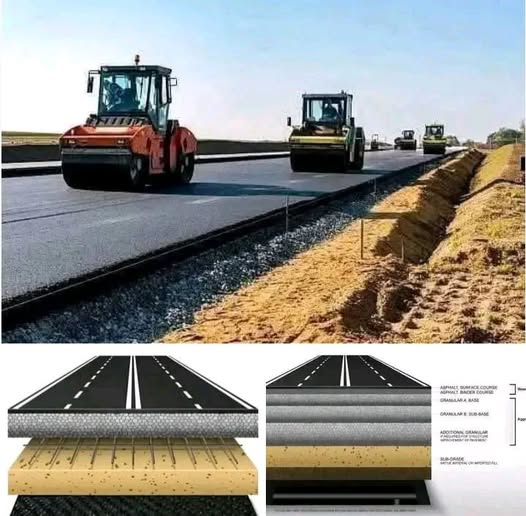
Building a Road :
New Road / Highway is constructed in 6 layers . Layer 1 – Sub Grade ( natural Soil – well compacted usually 60cm ) . Layer 2 – Sub base ( crushed stones 30cm ) . Layer 3 – Base Course ( Crushed Aggregate – 20cm ) Layer 4 – Bitumen Macadam – (10cm Asphalt with Lean bitumen Mix ) . Layer 5 – Dense Bitumen Macadam – ( 6cm of Rich asphalt ) . Layer 6 – Wearing Course ( 4cm of top layer of rich Asphalt ) .
Potholes :
Potholes form when water seeps into cracks in an asphalt road, saturates the underlying soil, and then freezes and expands in colder weather, weakening the break apart, and crumble, creating the pothole. This process is accelerated by repeated freeze-thaw pavement. The weight of traffic passing over this softened, weakened base causes the road surface to collapse, cycles and high traffic volume, leading to a feedback loop where the road becomes progressively weaker day by day.

The process of pothole formation:
- Cracking: Asphalt roads develop small cracks due to traffic, sunlight, rain, and temperature fluctuations.
- Water infiltration: Water from rain or snowmelt seeps through these cracks into the subgrade, the soil beneath the asphalt.
- Soil weakening: The water saturates and softens the soil, weakening its ability to support the road.
- Freeze-thaw cycles: In colder temperatures, the water freezes and expands, pushing the pavement upwards. When the ice melts, it leaves behind voids and a more saturated, weakened base.
- Traffic stress: The weight of vehicles passing over the now weakened area causes the pavement to deflect and break.
- Pavement failure: Repeated stress from traffic on the weak spot causes the asphalt to break off and crumble, creating a pothole.

Factors that worsen the problem:
- Temperature fluctuations:
Rapid shifts between freezing and thawing accelerate the weakening of the road’s base.
- Traffic volume:
The constant stress from vehicles passing over a weak spot can quickly turn a small defect into a large pothole.
- Poor drainage:
A lack of adequate drainage for water to escape can leave the subgrade saturated and vulnerable.

Causes of Bad Road Quality in India
Poor Indian road quality stems from factors like the use of substandard materials, insufficient quality, poor drainage, inadequate design, unqualified Engg team and corruption. These issues lead to faster road deterioration control, safety hazards like accidents and potholes, increased maintenance costs, and contribute to the overall poor state of the road network. Solutions include enforcing strict quality control, improving drainage, better engineering and design, ensuring accountability, and promoting a culture of civic responsibility for public infrastructure.
Reasons for Poor Road Quality –
- Substandard Materials & Construction:
Low-quality materials and inadequate construction practices, often due to cost-cutting, lead to roads that deteriorate rapidly.
- Poor Quality Control:
A lack of strict quality control during procurement and construction means materials and workmanship may not meet required standards.
- Corruption:
Corruption at various levels, including among political leaders and in the awarding of contracts, diverts funds and leads to poor-quality road projects.
- Inadequate Drainage:
Poorly designed cross-slopes and insufficient drainage systems result in stagnant water, causing potholes and road damage. Standing water in the road is the killer of good roads .
- Faulty Road Design:
Defective road engineering, poor design of junctions, and inadequate safety features, such as crash barriers and rumble strips, contribute to accidents.
- Lack of Maintenance:
Routine maintenance is often neglected, allowing roads to degrade significantly.
- Heavy Traffic & Overloading:
Overloaded trucks and excessive traffic also contribute to the rapid wear and tear of roads.

Potential Solutions –
- Strict Quality Control:
Implementing robust quality assurance (QA/QC) measures and using technology like smart sensors and drones can ensure material quality and construction standards. Designated approve Asphalt Lab is requited for quality check.
- Improved Engineering and Design:
Focusing on better road design, proper curves, visibility, and safety features can significantly improve safety.
- Better Drainage Systems:
Ensuring proper cross-slopes and adequate drainage will prevent water accumulation and reduce pothole formation.
- Accountability and Transparency:
Holding contractors, consultants, and government agencies accountable for deficiencies in design and construction is crucial.
- Civic Sense and Responsibility:
Encouraging a culture of civic responsibility and respect for public property can help keep roads clean and well-maintained.
- Regular Maintenance:
Small cracks and potholes if aren’t fixed early, lead to bigger damage.
Quality check Asphalt and mix design –
In essence, the quality of the asphalt mix, proper layering, and construction techniques directly impact the road’s ability to perform as intended, ensuring safety, longevity, and cost-effectiveness for users.
The appropriate bitumen grade for asphalt road construction depends on climate and traffic load, with popular choices being VG-30 (Viscosity Grade) and the equivalent 60/70 penetration grade for general paving in India. Softer grades like VG-10 (80/100 penetration) are used in colder areas or for low-traffic roads.
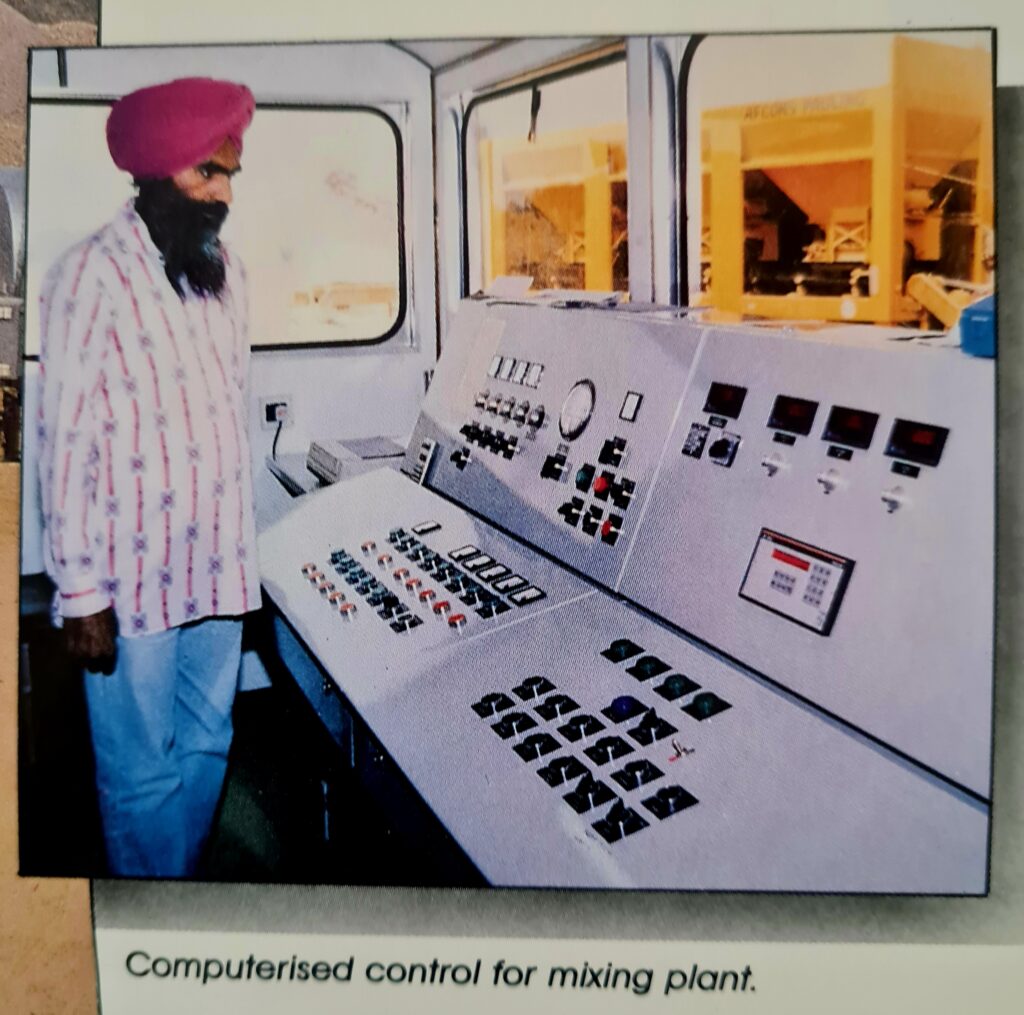

The quality of Bitumen supply in road from refineries is a question marks in India . It is not sure one get what a contractor order. Continuous in-house lab test is required to do the penetration check and design for a required mix strength. We have seen Indian roads bleeding in Summer due to poor quality bitumen , bad asphalt mix design and construction techniques.

Why Potholes ? –
Poor construction, inadequate compaction during paving, and substandard materials can also make roads more susceptible to developing potholes.
Potholes form when water seeps into cracks in an asphalt road, saturates the underlying soil, and then freezes and expands in colder weather, weakening the pavement. The weight of traffic passing over this softened, weakened base causes the road surface to collapse, break apart, and crumble, creating the pothole. This process is accelerated by repeated freeze-thaw cycles and high traffic volume, leading to a feedback loop where the road becomes progressively weaker.
The Pothole Formation Process –
- Surface Cracks:
Minor surface cracks allow water to enter the pavement structure.
- Water infiltration:
Water from rain or snowmelt seeps through these cracks into the subgrade, the soil beneath the asphalt.
- Weakened Base:
Water softens and erodes the soil in the base and subgrade layers, creating voids and reducing support for the asphalt above.
- Soil weakening:
The water saturates and softens the soil, weakening its ability to support the road.
- Fatigue and Failure:
Repeated stress from traffic on the poorly supported asphalt causes it to break apart and crumble.
- Freeze-thaw cycles:
In colder temperatures, the water freezes and expands, pushing the pavement upwards. When the ice melts, it leaves behind voids and a more saturated, weakened base.
- Traffic stress:
The weight of vehicles passing over the now weakened area causes the pavement to deflect and break.

- Pavement failure:
Repeated stress from traffic on the weak spot causes the asphalt to break off and crumble, creating a pothole.
- Temperature fluctuations:
Rapid shifts between freezing and thawing accelerate the weakening of the road’s base.
Traffic volume:
The constant stress from vehicles passing over a weak spot can quickly turn a small defect into a large pothole.
Poor drainage:
A lack of adequate drainage for water to escape can leave the subgrade saturated and vulnerable.
Once a small pothole is formed , with running traffic it become bigger and deeper chipping of top layer of road and then layer beneath with movement of traffic load in a matter of weeks. Potholes get bigger if not repaired properly.

What to do to eliminate potholes –
To reduce potholes, authorities should focus on proper road construction with good drainage, implement routine preventative maintenance like sealcoating, and embrace advanced techniques such as self-healing asphalt and improved utility management. They must also ensure contractor accountability for quality work, involve local communities in monitoring, and promote transparent, efficient grievance redressal systems for citizens.
Proactive Measures:
- Better Road Design:
Incorporate proper drainage with well-designed surfaces, shoulders, and storm drains to prevent water from reaching the road’s base and causing damage.
- Improved Construction Practices:
Use the latest technology and equipment during construction to ensure quality. Allow city planning and construction only after all underground civil work, such as laying water and sewage pipelines, is completed to prevent future road damage.
- Preventive Maintenance:
Conduct regular maintenance, including sealcoating, to create a protective layer on asphalt surfaces. This seals cracks and prevents water from seeping in, which is a common cause of potholes.
- Advanced Materials:
Investigate and adopt technologies like self-healing asphalt, which can repair small cracks automatically, extending road lifespan and reducing repair frequency.

Accountability and Monitoring:
- Contractor and Official Accountability:
Hold contractors and officials accountable for the quality of road work. Implement penalties for defaults and ensure transparency by displaying details of the work, estimated timeframes, and contact numbers for grievances.
- Resident Involvement:
Involve local residents by including them in monitoring committees and fostering regular interaction to address issues promptly.
- Grievance Redressal:
Establish and promote efficient grievance redressal mechanisms at municipal and central levels (e.g., through portals) to allow citizens to report problems and receive timely responses.

Long-Term Solutions:
- Shift from Patching to Permanent Repairs:
Move beyond temporary patching to permanent fixes by replacing the entire compromised area.
- Technology Integration:
Leverage technology to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of road repair work, thereby reducing costs and enhancing road safety.
In addition to good quality technique for road construction , drainage systems are crucial for healthy roads by preventing water damage to the road structure and foundation, ensuring road safety, improving traffic flow, and extending the road’s lifespan. By quickly removing surface water, drainage prevents conditions like hydroplaning and soil erosion that lead to cracks, potholes, and overall structural failure.

My opinion –
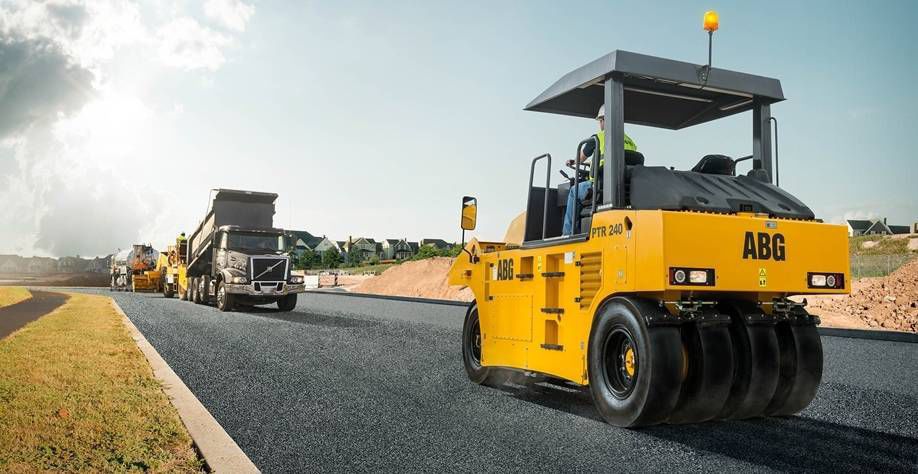
I have worked and seen world class roads projects internationally, can say that India is 15-20 years behind to construct and maintain good quality pothole free roads . Laying another layer of Asphalt on top of old damaged dusty filthy road and full of potholes is not a solution. By using milling technique, the old road should be scarified and then laid with a fresh layer of Asphalt road under strict quality control. I do have opportunity and experience to works with British construction co. on a pioneer road project on NH-1 in India. I was told that the road constructed by my company was 10 year Maintenace free due to high quality check and construction.

Note- Asphalt mix is produced in hot mix plant at 180 Degree centigrade , laid and compacted at road site between 160 to 130 degree. But light traffic is only allowed when asphalt temp goes down to 50 Degree or after 48 hours , but in India the traffic start 6-8 hours !!
How many contractors have automatic hot mix plant ?. How many people have seen PTR roller while construction of a new road ? How many road contractors in India have an independent full fledge Asphalt lab for quality check ? Questions are many, but I fear we lack basic knowledge and knack to construct a good road which should last at least 3-4 monsoon rains.
Thanks for reading .
Read my other blogs at https://nriblogbuster.com/